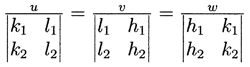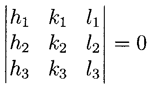Difference between revisions of "Zone axis"
From Online Dictionary of Crystallography
AndreAuthier (talk | contribs) |
AndreAuthier (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 15: | Line 15: | ||
[[image:Zoneaxis-2.png|center]] | [[image:Zoneaxis-2.png|center]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | == See also == | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Miller indices]]<br> | ||
| + | [[reciprocal lattice]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ---- | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Category:Fundamental crystallography]]<br> | ||
Revision as of 09:33, 4 February 2006
Axe de zone (Fr). Zonenachse (Ge). Eje de zona (Sp). Ось зоны (Ru).
A zone axis is a lattice row parallel to the intersection of two (or more) families of lattices planes. It is denoted by [u v w]. A zone axis [u v w] is parallel to a family of lattice planes of Miller indices (hkl) if:
uh + vk + wl = 0
The indices of the zone axis defined by two lattice planes ([math] h_1, k_1, l_1 [/math]), ([math] h_2, k_2, l_2[/math]) are given by:
Three lattice planes have a common zone axis (are in zone) if their Miller indices ([math] h_1, k_1, l_1 [/math]), ([math] h_2, k_2, l_2[/math]), ([math] h_3, k_3, l_3[/math]) satisfy the relation:
See also
Miller indices
reciprocal lattice