Difference between revisions of "Bravais-Miller indices"
From Online Dictionary of Crystallography
AndreAuthier (talk | contribs) |
AndreAuthier (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
== Definition == | == Definition == | ||
| − | The Bravais-Miller indices are used in the case of hexagonal lattices. In that case, one uses four axes, '''a<sub>1</sub>''', '''a<sub>2</sub>''', '''a<sub>3</sub>''', '''c''' and four [[Miller indices]], (''hkil''), where ''h'', ''k'', ''i'', ''l'' are prime integers inversely proportional to the intercepts of a plane of the family with the four axes. The indices ''h'', ''k'', ''i'' are cyclically permutable and related by | + | The Bravais-Miller indices are used in the case of hexagonal lattices. In that case, one uses four axes, '''a<sub>1</sub>''', '''a<sub>2</sub>''', '''a<sub>3</sub>''', '''c''' and four [[Miller indices]], (''hkil''), where ''h'', ''k'', ''i'', ''l'' are prime integers inversely proportional to the intercepts ''OP'', ''OQ'', ''OS'', ''OR'' of a plane of the family with the four axes. The indices ''h'', ''k'', ''i'' are cyclically permutable and related by |
<center> | <center> | ||
''h'' + ''k'' + ''i'' = 0 | ''h'' + ''k'' + ''i'' = 0 | ||
</center> | </center> | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:MILLER-3.gif|center]] | ||
== see also == | == see also == | ||
Revision as of 15:18, 3 February 2006
(French: Indices de Bravais-Miller. Spanish: Indices de Bravais-Miller.)
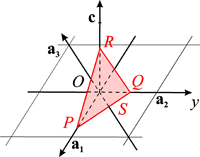
Definition
The Bravais-Miller indices are used in the case of hexagonal lattices. In that case, one uses four axes, a1, a2, a3, c and four Miller indices, (hkil), where h, k, i, l are prime integers inversely proportional to the intercepts OP, OQ, OS, OR of a plane of the family with the four axes. The indices h, k, i are cyclically permutable and related by
h + k + i = 0