Difference between revisions of "Bravais-Miller indices"
From Online Dictionary of Crystallography
BrianMcMahon (talk | contribs) m (Style edits to align with printed edition) |
BrianMcMahon (talk | contribs) m (Tidied translations.) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | <font color="blue">Indices de Bravais-Miller</font> (''Fr''). <font color=" | + | <font color="blue">Indices de Bravais-Miller</font> (''Fr''). <font color="black">Indici di Bravais-Miller</font> (''It''). <font color="purple">ブラベー・ミラー指数</font> (''Ja''). <font color="green">Indices de Bravais-Miller</font> (''Sp''). |
<Font color="black"> | <Font color="black"> | ||
Latest revision as of 16:46, 9 November 2017
Indices de Bravais-Miller (Fr). Indici di Bravais-Miller (It). ブラベー・ミラー指数 (Ja). Indices de Bravais-Miller (Sp).
Definition
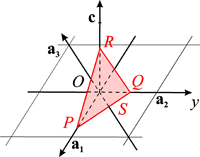
For trigonal and hexagonal crystals, it is useful to use a reference built on four axes, three in the plane normal to the unique axis (a1, a2, a3) and one ( c) for the unique axis. Consequently, four indices of lattice planes (hkil) are used, called the Bravais-Miller indices. Here h, k, i, l are integers inversely proportional to the intercepts of a plane of the family with the four axes. Only two of the three axes in a plane are linearly independent: a3 is expressed as a3 = -a1-a2. Analogously, the indices h, k, i are cyclically permutable and related by
h + k + i = 0.