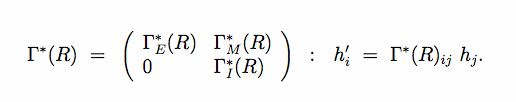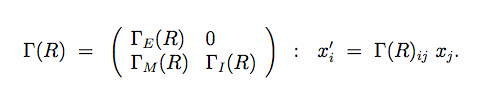Difference between revisions of "Superspace point group"
From Online Dictionary of Crystallography
BrianMcMahon (talk | contribs) m (Style edits to align with printed edition) |
BrianMcMahon (talk | contribs) (Tidied translations and added German and Spanish (U. Mueller)) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | < | + | <font color="blue">Groupe ponctuel de superespace</font> (''Fr''). <font color="red">Punktgruppe des Superraums</font> (''Ge''). <font color="black">Gruppo puntuale di superspazio</font> (''It''). <font color="purple">超空間の点群</font> (''Ja''). <font color="green">Grupo puntual del superespacio</font> (''Sp''). |
| + | |||
== Definition == | == Definition == | ||
Latest revision as of 09:17, 20 November 2017
Groupe ponctuel de superespace (Fr). Punktgruppe des Superraums (Ge). Gruppo puntuale di superspazio (It). 超空間の点群 (Ja). Grupo puntual del superespacio (Sp).
Definition
An (m+d)-dimensional superspace group is a space group with a point group K that leaves an m-dimensional (real) subspace invariant. Therefore, K is R-reducible and its elements are pairs ([math]R_E,~R_I[/math]) of orthogonal transformations. Both [math]R_E[/math] and [math]R_I[/math] may themselves be R-reducible in turn. They form the m-dimensional point group [math]K_E[/math], and the d-dimensional point group [math]K_I[/math], respectively.
Comments
On a lattice basis the point group elements are represented by integral matrices [math]\Gamma (R)[/math]. The action of the point group on the reciprocal lattice is given by the integral matrix [math]\Gamma^*(R)[/math], which is the inverse transpose of [math]\Gamma (R)[/math].
The diffraction spots of an aperiodic crystal belong to a vector module [math]M^*[/math] that is the projection of the n-dimensional reciprocal lattice [math]\Sigma^*[/math] on the physical space. The projections of the basis vectors [math]a_{si}^*[/math] of [math]\Sigma^*[/math] are the basis vectors [math]a_{si}^*[/math] of the vector module [math]M^*[/math]. Therefore, the action of the n-dimensional point group of the superspace group on the basis of [math]M^*[/math] is
[math]R_E a_i^* ~=~ \sum_{j=1}^n \Gamma^*(R)_{ij} a_j^* ,~~(i=1,\dots,n).[/math]
For an incommensurate modulated structure, the submodule of the main reflections is invariant. As a consequence, the elements of the point group in superspace in this case is Z-reducible. There is a basis such that the point group elements are represented by the integral matrices
Both [math]\Gamma_E^*(K)[/math] and [math]\Gamma_I^*(K)[/math] are integral representations of K, as are their conjugates [math]\Gamma_E(K)[/math] and [math]\Gamma_I(K)[/math].
Points in direct space, with lattice coordinates [math]x_1,\dots,x_n[/math] transform according to
In direct space the internal space [math]V_I[/math] is left invariant, and this subspace contains a d-dimensional lattice, that is left invariant.