Difference between revisions of "Acceptance domain"
From Online Dictionary of Crystallography
TedJanssen (talk | contribs) |
BrianMcMahon (talk | contribs) (Tidied translations and added German (U. Mueller)) |
||
| (8 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | + | Synonyms: window, atomic domain, atomic surfaces | |
| − | + | <font color="blue">Domaine d'acceptation, fenêtre</font> (''Fr''). <font color="red">Atomare Oberfläche, Akzeptanz-Domäne</font> (''Ge''). | |
| − | + | == Definition == | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
When an aperiodic crystalline point set is obtained by the intersection method, as the intersection of a periodic array of finite, disjoint components in superspace and the physical | When an aperiodic crystalline point set is obtained by the intersection method, as the intersection of a periodic array of finite, disjoint components in superspace and the physical | ||
| − | space, then there is, for each point , a component in the higher-dimensional | + | space, then there is, for each point, a component in the higher-dimensional |
unit cell. These components are called ''acceptance domains'', ''atomic surfaces'', ''atomic domains'', or ''windows'' in the literature. The positions of atoms in aperiodic crystals (or vertices in the case of a tiling) | unit cell. These components are called ''acceptance domains'', ''atomic surfaces'', ''atomic domains'', or ''windows'' in the literature. The positions of atoms in aperiodic crystals (or vertices in the case of a tiling) | ||
are the intersection of the atomic surfaces with the physical space. This construction of the | are the intersection of the atomic surfaces with the physical space. This construction of the | ||
points is called the ''intersection method''. | points is called the ''intersection method''. | ||
| − | + | == History == | |
The term ''window'' comes from an alternative construction. One considers a 'tube' | The term ''window'' comes from an alternative construction. One considers a 'tube' | ||
in ''n''-dimensional superspace | in ''n''-dimensional superspace | ||
that is the product of the ''m''-dimensional physical space ''V'' and a transversal finite (''n-m'')-dimensional object ''O'': | that is the product of the ''m''-dimensional physical space ''V'' and a transversal finite (''n-m'')-dimensional object ''O'': | ||
| − | + | <math>V\otimes O</math>. Then the points of the ''n''-dimensional lattice, corresponding | |
to the periodic embedding of the structure in ''V'', that lie inside the tube are projected | to the periodic embedding of the structure in ''V'', that lie inside the tube are projected | ||
| − | on ''V'' ( | + | on ''V'' (see figure). These are the points of the aperiodic structure in ''V''. |
The construction is called the ''cut-and-project method''. The object ''O'' | The construction is called the ''cut-and-project method''. The object ''O'' | ||
is the ''window'', or ''acceptance domain''. The latter expresses the fact that only | is the ''window'', or ''acceptance domain''. The latter expresses the fact that only | ||
| Line 31: | Line 29: | ||
[[Image:BO02F20.gif]] | [[Image:BO02F20.gif]] | ||
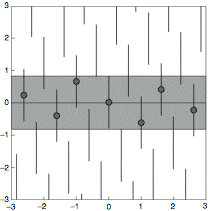
| − | + | The grey strip in superspace is the product of the (infinite) physical space (in this | |
case the horizontal line) and a vertical finite line interval, the acceptance domain. The centres | case the horizontal line) and a vertical finite line interval, the acceptance domain. The centres | ||
of the vertical lines form a lattice. When a lattice point falls inside the strip it is projected on the physical space. The projected points form an aperiodic crystal. These projected points are also the intersections of the array of vertical lines with the physical space. | of the vertical lines form a lattice. When a lattice point falls inside the strip it is projected on the physical space. The projected points form an aperiodic crystal. These projected points are also the intersections of the array of vertical lines with the physical space. | ||
| + | == See also == | ||
| + | *[[Atomic surface]] | ||
| + | |||
| − | + | [[Category: Fundamental crystallography]] | |
Latest revision as of 17:44, 8 November 2017
Synonyms: window, atomic domain, atomic surfaces
Domaine d'acceptation, fenêtre (Fr). Atomare Oberfläche, Akzeptanz-Domäne (Ge).
Definition
When an aperiodic crystalline point set is obtained by the intersection method, as the intersection of a periodic array of finite, disjoint components in superspace and the physical space, then there is, for each point, a component in the higher-dimensional unit cell. These components are called acceptance domains, atomic surfaces, atomic domains, or windows in the literature. The positions of atoms in aperiodic crystals (or vertices in the case of a tiling) are the intersection of the atomic surfaces with the physical space. This construction of the points is called the intersection method.
History
The term window comes from an alternative construction. One considers a 'tube' in n-dimensional superspace that is the product of the m-dimensional physical space V and a transversal finite (n-m)-dimensional object O: [math]V\otimes O[/math]. Then the points of the n-dimensional lattice, corresponding to the periodic embedding of the structure in V, that lie inside the tube are projected on V (see figure). These are the points of the aperiodic structure in V. The construction is called the cut-and-project method. The object O is the window, or acceptance domain. The latter expresses the fact that only lattice points inside the tube are projected. The result is the same as attaching a copy of O to each lattice point, and considering the intersection of this periodic array with V. Actually, the latter construction is more special, in the sense that the atomic surfaces in this are by definition flat, whereas the intersection method allows arbitrarily shaped ones.
The grey strip in superspace is the product of the (infinite) physical space (in this case the horizontal line) and a vertical finite line interval, the acceptance domain. The centres of the vertical lines form a lattice. When a lattice point falls inside the strip it is projected on the physical space. The projected points form an aperiodic crystal. These projected points are also the intersections of the array of vertical lines with the physical space.