Difference between revisions of "Derivative structure"
From Online Dictionary of Crystallography
(category) |
BrianMcMahon (talk | contribs) m (Minor typos and style changes) |
||
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
*the space group G’ of S is a subgroup of the space group G of S; | *the space group G’ of S is a subgroup of the space group G of S; | ||
*the translation lattice is preserved, ''i''.''e''. the translation subgroup T(G’) of S’ is the same as the translation subgroup T(G) of S; | *the translation lattice is preserved, ''i''.''e''. the translation subgroup T(G’) of S’ is the same as the translation subgroup T(G) of S; | ||
| − | *as a consequence, the point group | + | *as a consequence, the point group P’ of S’ is a subgroup of the point group P of S (''i''.''e''. S’ belong to a lower-symmetric geometric crystal class with respect to S); |
*at least one of the [[Wyckoff position]]s of S is split into two or more independent Wyckoff positions of S’ and the corresponding [[crystallographic orbit]]s are occupied by chemically different atoms. | *at least one of the [[Wyckoff position]]s of S is split into two or more independent Wyckoff positions of S’ and the corresponding [[crystallographic orbit]]s are occupied by chemically different atoms. | ||
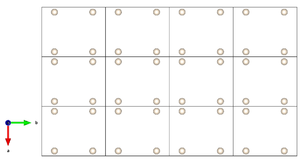
| − | [[Image:basic structure.png|right|thumb|A structure S composed | + | [[Image:basic structure.png|right|thumb|A structure S composed of a single crystallographic orbit]] |
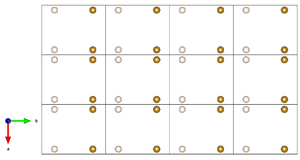
[[Image:derivative structure.png|right|thumb|A structure S' obtained from S by reducing its point symmetry while preserving its translation lattice. Atomic positions represented by a different colour are not equivalent in S' and are occupied by chemically different atoms. S is called a '''basic structure''', S' a '''derivative structure''' of S]] | [[Image:derivative structure.png|right|thumb|A structure S' obtained from S by reducing its point symmetry while preserving its translation lattice. Atomic positions represented by a different colour are not equivalent in S' and are occupied by chemically different atoms. S is called a '''basic structure''', S' a '''derivative structure''' of S]] | ||
== Notes == | == Notes == | ||
| − | The definition of derivative structure was introduced by Martin J. Buerger: ''Journal of Chemical Physics'' '''15''' | + | The definition of derivative structure was introduced by Martin J. Buerger (1947): ''Journal of Chemical Physics'', '''15''', 1-16. |
== See also == | == See also == | ||
Latest revision as of 12:50, 15 July 2021
Structure dérivative (Fr). Struttura derivativa (It).
A derivative structure is a crystal structure S’ obtained from another crystal structure (called a basic structure) S under the following conditions:
- the space group G’ of S is a subgroup of the space group G of S;
- the translation lattice is preserved, i.e. the translation subgroup T(G’) of S’ is the same as the translation subgroup T(G) of S;
- as a consequence, the point group P’ of S’ is a subgroup of the point group P of S (i.e. S’ belong to a lower-symmetric geometric crystal class with respect to S);
- at least one of the Wyckoff positions of S is split into two or more independent Wyckoff positions of S’ and the corresponding crystallographic orbits are occupied by chemically different atoms.
Notes
The definition of derivative structure was introduced by Martin J. Buerger (1947): Journal of Chemical Physics, 15, 1-16.