Difference between revisions of "Group homomorphism"
From Online Dictionary of Crystallography
(some small adjustments) |
(definition of a group replaced by a link to a separate definition) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
<font color="blue">Homomorphisme de groupes </font> (''Fr''). <font color="red">Gruppenhomomorphismus</font> (''Ge''). <font color="green">Homomorfismo de grupos </font> (''Sp''). <font color="black">Omomorfismo di gruppi </font> (''It''). <Font color="purple">準同形</font> (''Ja''). | <font color="blue">Homomorphisme de groupes </font> (''Fr''). <font color="red">Gruppenhomomorphismus</font> (''Ge''). <font color="green">Homomorfismo de grupos </font> (''Sp''). <font color="black">Omomorfismo di gruppi </font> (''It''). <Font color="purple">準同形</font> (''Ja''). | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
==Homomorphism between groups== | ==Homomorphism between groups== | ||
| − | A '''group homomorphism''' from (''G'', *) to (''H'', #) is a [[mapping]] ''f'' : ''G'' → ''H'' that preserves the composition law, | + | A '''group homomorphism''' from a [[group]] (''G'', *) to a [[group]] (''H'', #) is a [[mapping]] ''f'' : ''G'' → ''H'' that preserves the composition law, i.e. for all ''u'' and ''v'' in ''G'' one has: |
<div align="center"> | <div align="center"> | ||
''f''(''u'' * ''v'') = ''f''(''u'') # ''f''(''v''). | ''f''(''u'' * ''v'') = ''f''(''u'') # ''f''(''v''). | ||
Revision as of 14:46, 1 April 2009
Homomorphisme de groupes (Fr). Gruppenhomomorphismus (Ge). Homomorfismo de grupos (Sp). Omomorfismo di gruppi (It). 準同形 (Ja).
Contents
[hide]Homomorphism between groups
A group homomorphism from a group (G, *) to a group (H, #) is a mapping f : G → H that preserves the composition law, i.e. for all u and v in G one has:
f(u * v) = f(u) # f(v).
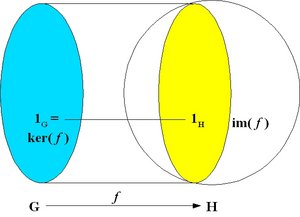
A homomorphism f maps the identity element 1G of G to the identity element 1H of H, and it also maps inverses to inverses: f(u-1) = f(u)-1.
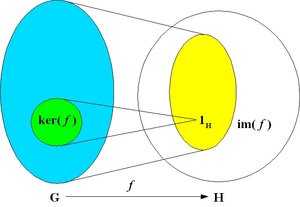
Kernel and image
The kernel of the homomorphism f is the set of elements of G that are mapped to the identity of H:
ker( f ) = { u in G : f(u) = 1H }
The image of the homomorphism f is the subset of elements of H to which at least one element of G is mapped by f:
im( f ) = { f(u) : u in G }.
The kernel is a normal subgroup of G and the image is a subgroup of H.
Types of homomorphisms
Homomorphisms can be classified according to different criteria, among which the relation between G and H and the nature of the mapping.
Surjective, injective and bijective homomorphisms
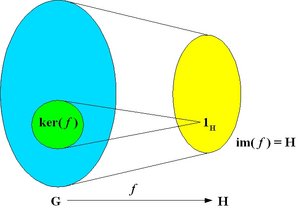
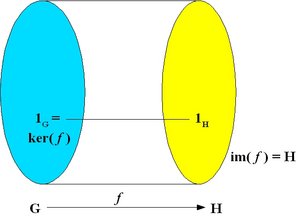
An epimorphism is a surjective homomorphism, that is, a homomorphism which is onto as a mapping. The image of the homomorphism is the whole of H, i.e. im( f ) = H
A monomorphism is an injective homomorphism, that is, a homomorphism which is one-to-one as a mapping. In this case, ker( f ) = {1G }.
If the homomorphism f is a bijection, then its inverse is also a group homomorphism, and f is called an isomorphism; the groups (G,*) and (H,#) are called isomorphic and differ only in the notation of their elements (and possibly their binary operations), while they can be regarded as identical for most practical purposes.
Homomorphisms from a group to itself (G = H)
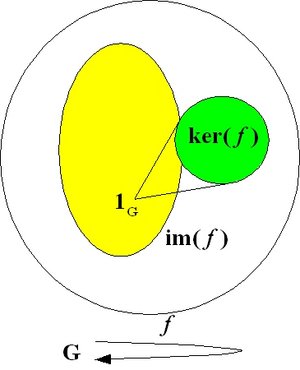
.An endomorphism is a homomorphism of a group to itself: f: G → G.
A bijective (invertible) endomorphism (which is hence an isomorphism) is called an automorphism. The kernel of the automorphism is the identity of G (1G) and the image of the automorphism coincides with G. The set of all automorphisms of a group (G,*) forms itself a group, the automorphism group of G, Aut(G).