Difference between revisions of "Wigner-Seitz cell"
From Online Dictionary of Crystallography
TedJanssen (talk | contribs) m (→Definition) |
BrianMcMahon (talk | contribs) m |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
<Font color="blue"> Maille de Wigner-Seitz </Font>(''Fr''). <Font color="red"> Wigner-Seitz Zell </Font>(''Ge''). <Font color="green"> Celda de Wigner-Seitz</Font> (''Sp'').<Font color="black"> Cella di Wigner-Seitz </Font>(''It'') | <Font color="blue"> Maille de Wigner-Seitz </Font>(''Fr''). <Font color="red"> Wigner-Seitz Zell </Font>(''Ge''). <Font color="green"> Celda de Wigner-Seitz</Font> (''Sp'').<Font color="black"> Cella di Wigner-Seitz </Font>(''It'') | ||
| − | |||
== Definition == | == Definition == | ||
| Line 22: | Line 21: | ||
Section 1.5 of ''International Tables of Crystallography, Volume B''<br> | Section 1.5 of ''International Tables of Crystallography, Volume B''<br> | ||
Sections 1.2 and 2.2 of ''International Tables of Crystallography, Volume D''<br> | Sections 1.2 and 2.2 of ''International Tables of Crystallography, Volume D''<br> | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
[[Category:Fundamental crystallography]]<br> | [[Category:Fundamental crystallography]]<br> | ||
Revision as of 12:09, 8 February 2012
Maille de Wigner-Seitz (Fr). Wigner-Seitz Zell (Ge). Celda de Wigner-Seitz (Sp). Cella di Wigner-Seitz (It)
Definition
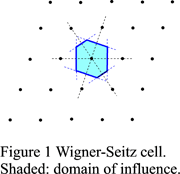
The Wigner-Seitz cell is a a polyhedron obtained by connecting a lattice point P to all other lattice points and drawing the planes perpendicular to these connecting lines and passing through their midpoints (Figure 1). The polyhedron enclosed by these planes is the Wigner-Seitz cell. This construction is called the Dirichlet construction. The cell thus obtained is a primitive cell and it is possible to fill up the whole space by translation of that cell.
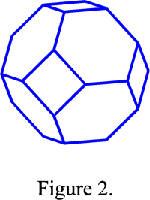
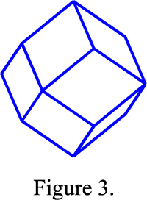
The Wigner-Seitz cell of a body-centred cubic lattice I is a cuboctahedron (Figure 2) and the Wigner-Seitz cell of a face-centred cubic lattice F is a rhomb-dodecahedron (Figure 3). In reciprocal space this cell is the first Brillouin zone. Since the reciprocal lattice of body-centred lattice is a face-centred lattice and reciprocally, the first Brillouin zone of a body-centred cubic lattice is a rhomb-dodecahedron and that of a face-centred cubic lattice is a cuboctahedron.
The inside of the Wigner-Seitz cell has been called domain of influence by Delaunay (1933). It is also called Dirichlet domain or Voronoi domain. The domain of influence of lattice point P thus consists of all points Q in space that are closer to this lattice point than to any other lattice point or at most equidistant to it (such that OP ≤ |t - OP| for any vector t ∈ L).
See also
Section 9.1 of International Tables of Crystallography, Volume A
Section 1.5 of International Tables of Crystallography, Volume B
Sections 1.2 and 2.2 of International Tables of Crystallography, Volume D